Day 2: The map helper

The map() helps to make a new array from the elements of the given array by performing some action on each element.
In simple language, The map helper takes a function as the argument and performs that function on each element of the given array (in order of index) to create a new array without changing the original array.
Example
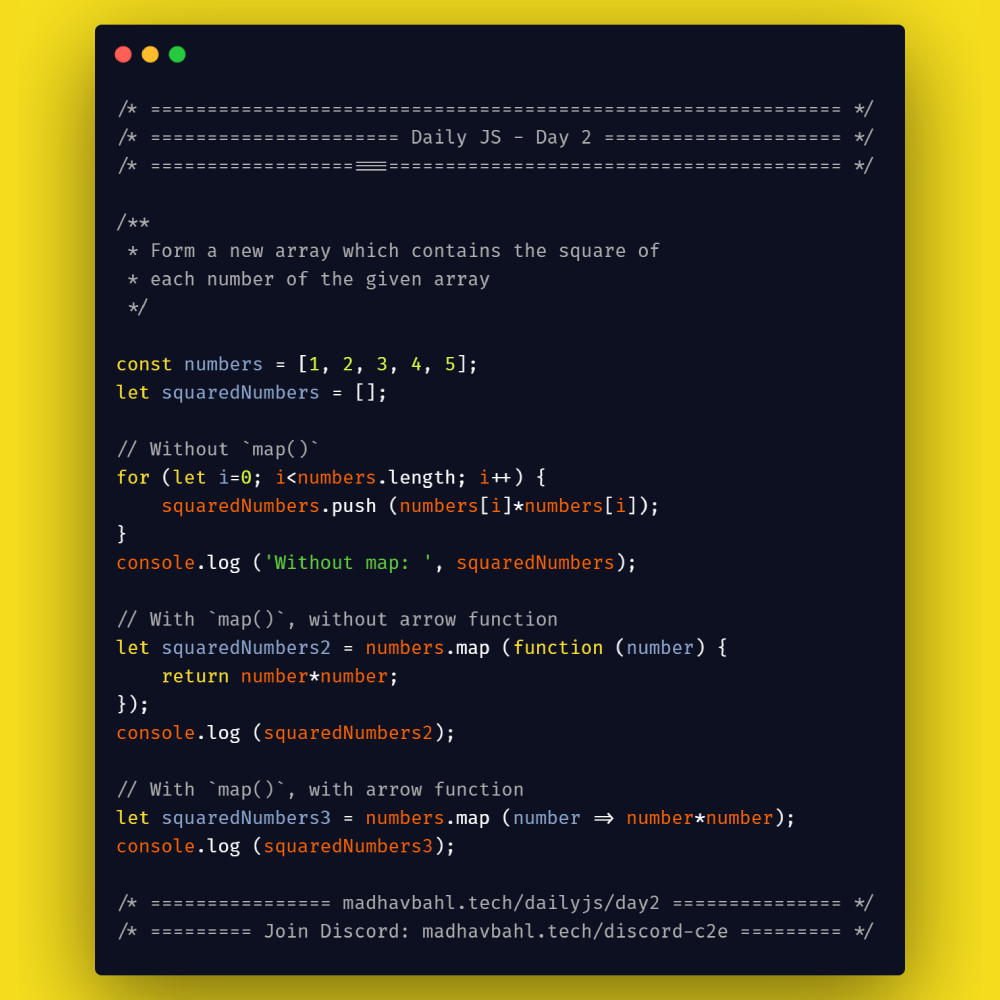
Form a new array which contains the square of each number of the given array
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let squaredNumbers = [];
// Without `map()`
for (let i=0; i<numbers.length; i++) {
squaredNumbers.push (numbers[i]*numbers[i]);
}
console.log ('Without map: ', squaredNumbers);
// With `map()`, without arrow function
let squaredNumbers2 = numbers.map (function (number) {
return number*number;
});
console.log ('With map, without arrow function', squaredNumbers2);
// With `map()`, with arrow function
let squaredNumbers3 = numbers.map (number => number*number);
console.log ('With map, with arrow function', squaredNumbers3);
Syntax
array.map(function(currentValue, index, arr), thisValue)
- currentValue: Required. The value of the current element.
- index: Optional. The array index of the current element.
- arr: Optional. The array object the current element belongs to.
Why creating a new array is a good practise
When the code base is small, we tend to perform all the actions on the same data structure and feel free to change it easily because we know wherever it is being used, but when the code base becomes huge and we are not sure whether a given data structure is being used at other place or not, it is not good to change it directly as it might lead to some inconsistencies at the other places where it is being used
Generally, we try not to mutate any given data structure, because it’s possible that the given data structure could have been used in some other place as well and changing it might break our code.
The map helper comes to the rescue at such places, it applies a particular function to each element in an array and return a new array without changing the original one.
Practise questions
-
Make an array of numbers that are doubles of the first array
-
Take an array of numbers and convert each element into a string
Download your free eBook
Carbon code sample